Back pain is a common ailment that many individuals experience at some point in their lives. While most cases of back pain are temporary and manageable, there can be instances where back pain is associated with other health issues, such as urinary incontinence. In this blog post, we will delve into the relationship between back pain and bladder leakage, exploring pelvic floor muscles, herniated discs, cauda equina syndrome, and more.
- The connection between back pain and urinary incontinence
- Herniated discs and nerve compression
- Pelvic floor muscles and bladder control
- Risk factors and preventative measures
- Seeking medical advice and interventions
- Additional resources
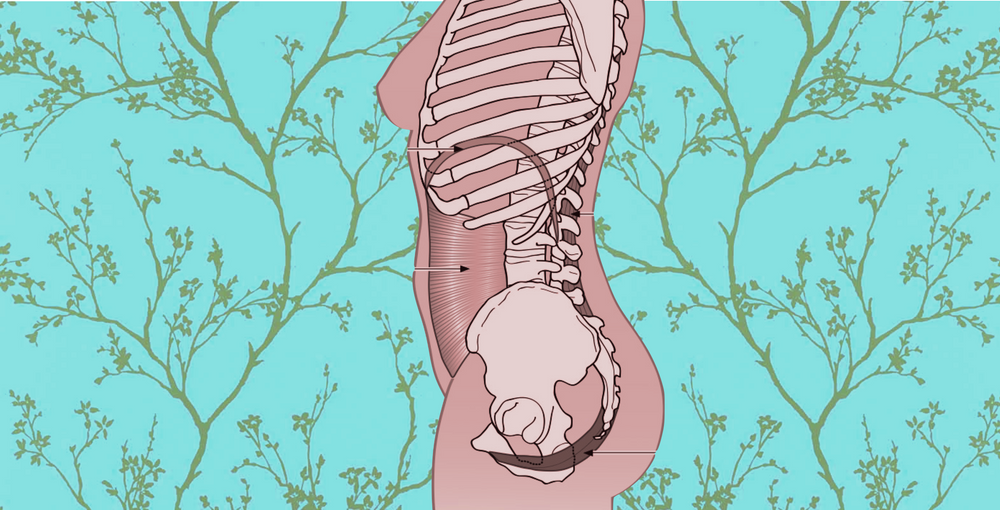
Pelvic Floor Muscles and Back Pain
To start, it’s important to understand the link between the pelvic floor muscles and back pain. Pelvic floor muscles create the base of the muscles otherwise known as one’s “core.” These core muscles work to support the abdomen, diaphragm, and back muscles, where they support the spine. The job of the core muscles is to support the torso and to stabilize it with movement. If they are not working properly, the torso and pelvis become unstable and you’re more likely to experience back pain and posterior pelvic pain in the “SI joints" or sacroiliac joints, which link the pelvis with the lower spine.
Herniated Discs, Nerve Compression, and the Connection Between UI and Back Pain
Furthermore, herniated discs, often a cause of lower back pain or lumbar pain, occur when the soft inner material of a spinal disc pushes through its outer layer. This can result in nerve compression, which can lead to not only back pain but also nerve damage that affects various bodily functions, including bladder control. When a herniated disc presses against nerves that control the bladder and surrounding muscles, it can cause issues like urge incontinence and even bowel incontinence. Additionally, cauda equina syndrome (CES), a serious condition resulting from the compression of the nerve roots at the base of the spinal cord. CES can lead to various dysfunctions, including both urinary and bowel incontinence, making it a medical emergency that needs intervention.
Risk Factors and Preventive Measures
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of experiencing back pain and subsequent urinary incontinence. Obesity, which strains the back muscles and spine, is a common cause. Also, spinal cord injuries, kidney stones, and even prostate cancer treatments can lead to back pain and potential nerve damage. Practicing proper posture, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of both back pain and incontinence.
Seeking Medical Advice and Interventions
If you experience back pain accompanied by urinary incontinence, it's essential to consult health care professionals promptly. They can assess your condition and recommend appropriate interventions, which might include physical therapy for muscle training and strengthening, as well as medications or surgeries if necessary. In cases where a serious condition like CES or spinal tumors is suspected, quick medical attention is crucial to prevent further complications.
Conclusion
The correlation between back pain and urinary incontinence is a complex and multi-faceted issue. While some cases might be due to simple muscle strain, it's important to recognize that the combination of back pain and incontinence could signify underlying conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or nerve compression. By staying proactive about spine health, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can minimize the risk of experiencing these discomforts and ensure a better quality of life.
Want to learn more about back pain and incontinence?
- Conditions That Can Cause UI
- Signs of a Weak Pelvic Floor and Prevention
- Is There a Link Between Back Pain and Urinary Symptoms?
- Urinary Incontinence, Mayo Clinic